Why Why Analysis | Template | 5 Why Analysis Method with Manufacturing Examples
Last updated on January 1st, 2024 at 04:15 pm
Why Why Analysis | Excel Template | 5 Why Analysis Method with Manufacturing Examples
Hello readers! Today we are going to discuss and learn a popular topic, which is very useful and needful in the manufacturing industry to identify the root cause and to improve the operations. It’s nothing is called Why Why Analysis. In this topic, we are trying to cover the advanced concept and practical manufacturing examples for better understanding and easy implementation in operations. You can also download the Why Why Analysis excel template from the below given link.
Sample Why Why Analysis excel Template-DOWNLOAD.
Why Why Analysis Format-Download
5 Why Analysis Format-Download
Why Why Analysis Concept:
A Why Why Analysis is a very useful problem-solving technique and that is also popularly known as the 5-Whys in process, service and manufacturing industries. The purpose of why why analysis is to identify the root cause of a particular problem, issue, defects, wastages, customer complaint, non-conformity, etc. by repeatedly asking the question “why”. The 5 Whys is a simple but effective technique, that is used in numerous areas, particularly in process improvement, Cost Reduction projects, and lean projects. The main aim is to get to the root cause of a problem, issues, defects, non-conformities, etc. so that we can take action to eliminate the root cause of the problem.
How to perform a Why Why Analysis or 5-Whys (Step by Step guide):
As we know that the concept itself indicating the 5 whys means we have to ask multiple times “why” to identify the root cause of a problem or issue. Below is the step-by-step guide on how to perform a why why analysis (5W / 5-whys analysis);
Team Creation:
You have to create a team in such a way that all required possible functions members should be present in the team, for example CFT team.
Problem Identification:
In this process, you have to identify the problem by using tools, techniques, and principles. we use many techniques and statistical tools in manufacturing industries to identify the problem, issue, potential causes, risk, defects, etc. The most popular and commonly used techniques, tools & methods in industries for the identification of problems, issues, defects, risk,s and non-conformity & gaps are inspection, SPC, QMS auditing, product testing, Process & product auditing, maintenance checking, layer auditing, etc. rather than these practices we also use many other methods to identify the risk, issue, problems through Risk and Issue identification, Data analysis, warranty analysis, customer complaint, field failure, etc.
Problem Statement:
Before defining the problem statement, if you have multiple problems then select the problem based on the criticality considering with severity, occurrence, and detection. Then next define the problem statement. The main purpose of the problem statement is to understand the depth and concept of the problem and, if possible represent it in a pictorial manner so that a complete idea will be developed on the problem statement. The importance of problem statement is very crucial in the time of brainstorming of problems for root cause identification. If the problem statement will not be cleared to all team members then, doing why why analysis will not be effective.
Brainstorming of Why-Why Analysis (5 Whys):
Brainstorming on why why analysis is a creative problem-solving technique that is generally used to identify the root cause of a problem by multiple times asking of “why” and to generate a solution to the root cause. It’s a team activity in which all CFT members will ask why on problem until to get the root cause of the problem.
The effective and general rules for brainstorming of why why analysis are given below but these are not limited to.
- Assemble the team members from different functions related to problematic areas.
- Think about a comfortable and conducive environment.
- Encourages the team members for open and free thinking about the brainstorming of problems.
- Give always more focus on root cause identification and solution generation.
- The mentor of the CFT team is supposed to set a specific time limit for the brainstorming section.
- Record the Root cause and solution ideas.
- Once you record the Root cause and ideas, if there is more than one solution idea then, prioritize the idea and develop the action plan (CAPA).
- Validate the action plan by sample trial and if accepted then do the mass trial and after getting the effective result you can implement it as a full phase. In some cases, you can validate by ISIR report also.
- Documentation: document the action plan, do the updation & standardize in relevant records or documents, for example, control plan, check sheet, FMEA, SOP, etc.
- Effective monitoring and Measurement.
- Horizontal deployment.
Steps of Why-Why analysis:
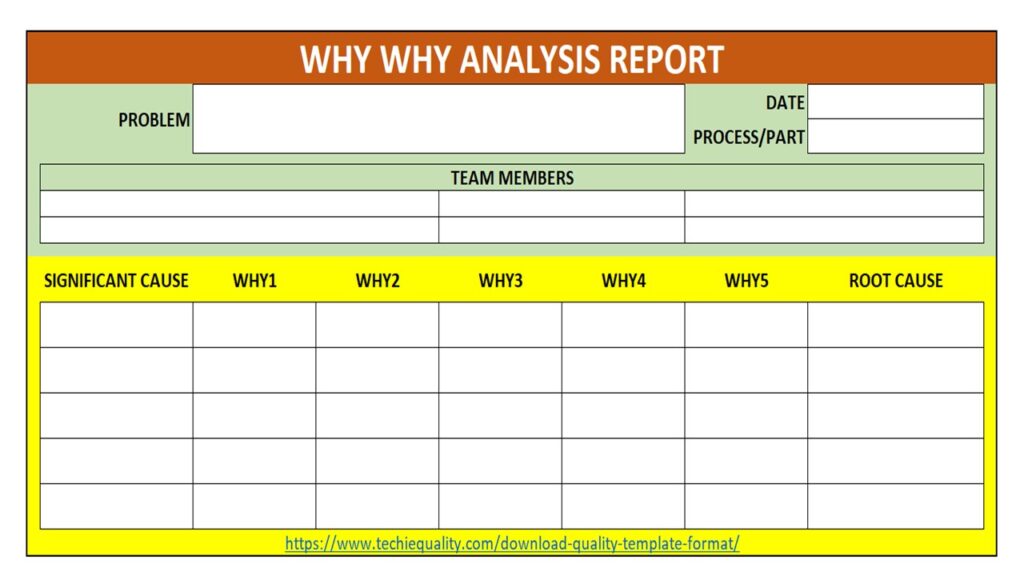
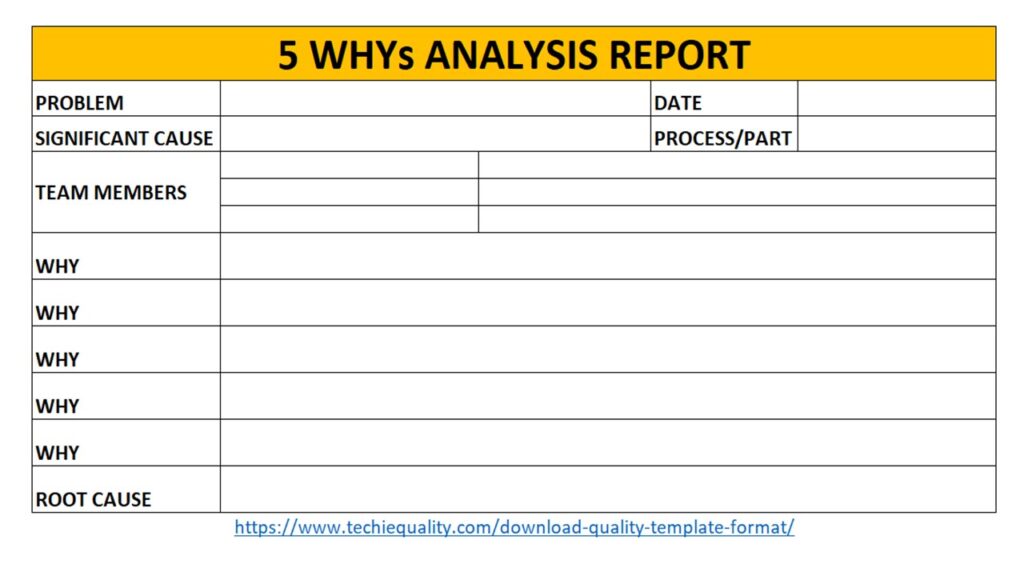
We have mentioned below two important templates or formats for both why why analysis and action plan formation in CAPA form. Let us learn the why why analysis first, as you can see in the first image (5 whys template) which is a very simple format where you have to write some basic information about the problem then you have to start asking “why” multiple times until find out the root cause. Once you identified the root cause then you should formulate a CAPA in CAPA format [see the second image in below].
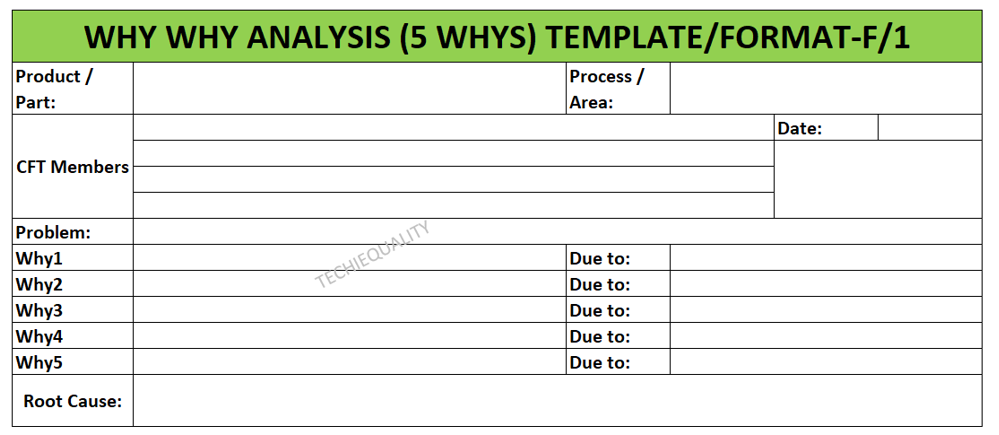
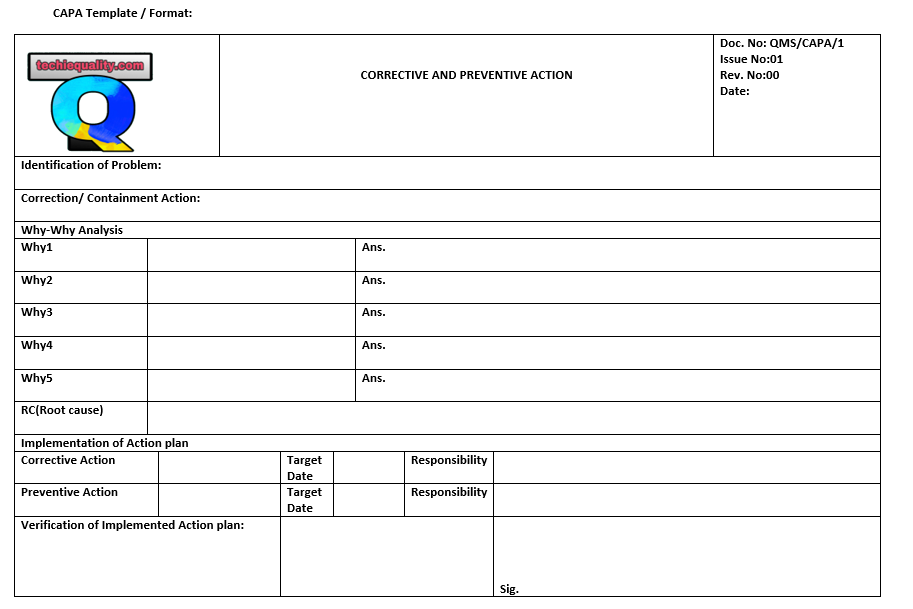
Steps of 5 whys analysis:
- Ask the first “why” to the problem and record the potential cause in “due to” or “Ans.” Row in the above format.
- Again ask “why” to the first potential cause and write down the “due to”.
- Repeat the process by asking “why” for each “due to” until you find the root cause.
Once you find out the root cause then, develop actionable solutions in CAPA format.

Manufacturing Example of Why Why Analysis:
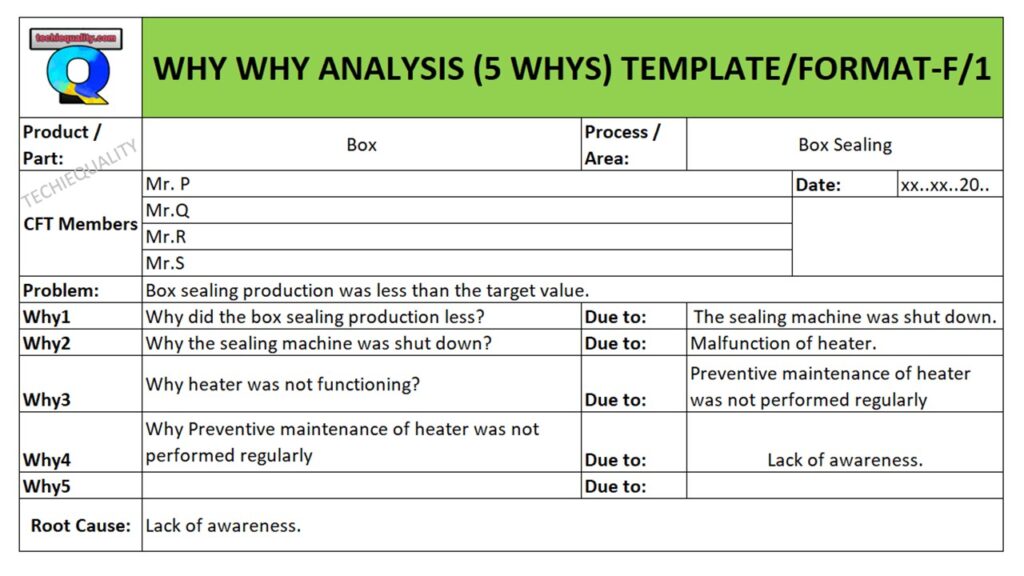
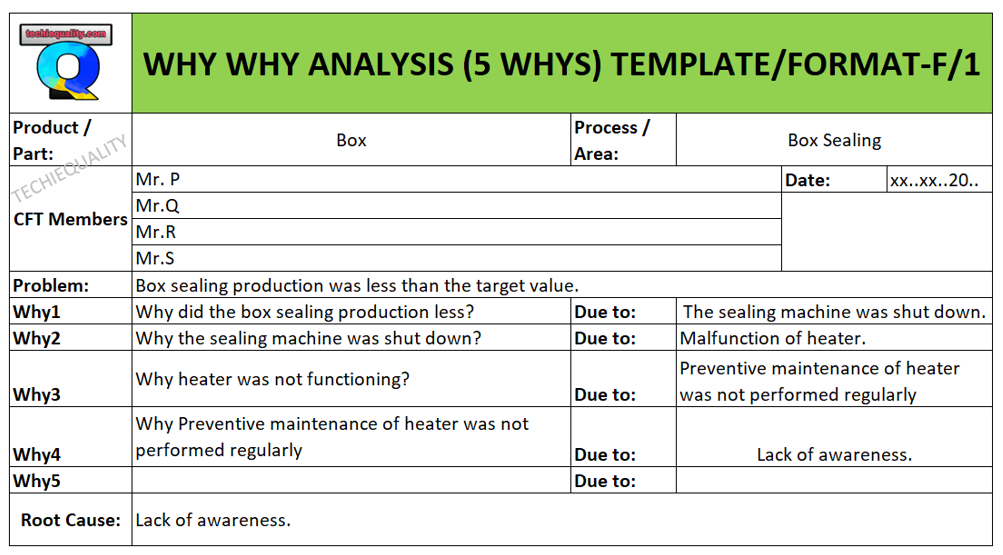
Problem: Box sealing production was less than the target value.
Why1: Why did the box sealing production less?
Due to: the sealing machine was shut down.
Why2: why the sealing machine was shut down?
Due to: Malfunction of heater.
Why3: why the heater was not functioning?
Due to: Preventive maintenance of heater was not performed regularly
Why4: Why Preventive maintenance of the heater was not performed regularly
Due to: Lack of awareness.
Root Cause: Lack of awareness.
We have filled up why why analysis template or format of the above example, which is given below for your better understanding.
Now the next process is the CAPA formation, we have already mentioned the CAPA format template in above, and same we are going to use it for action plan formation based on the above example, so let’s get started; if you would like to download the above template then click on the download link given in above.
CAPA Formation:
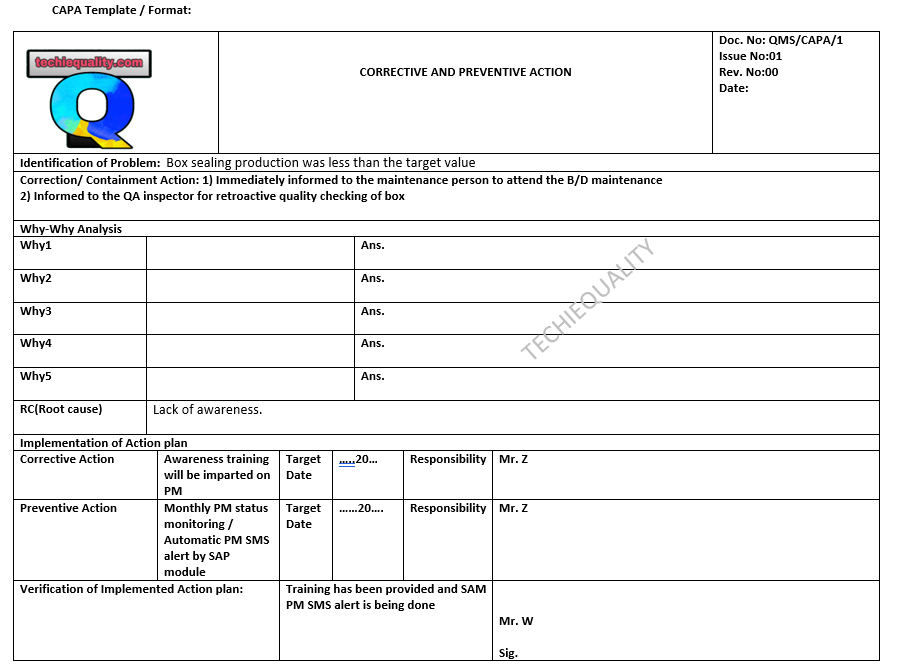
Problem: Box sealing production was less than the target value.
Root Cause: Lack of awareness.
Correction/ Containment Action: 1) Immediately inform to the maintenance person to attend the B/D maintenance. 2) Informed to the QA inspector for retroactive quality checking of the box.
Corrective Action: Awareness training will be imparted on PM (Preventive maintenance)
Preventive Action: Monthly PM status monitoring /Automatic PM SMS alert by SAP module
Go through the below filled-up format of CAPA format to understand the practical concept of Action plan formation.
Benefits of 5 Why Analysis:
There are several benefits of 5 whys analysis but some important are listed below
- To understand the issues/problems/ defects, etc.
- Identify the root cause of a problem.
- Prevent recurrence.
- Continuous Improvement
- Enhancing the innovation
- Helps in decision-making
- Helps in risk management
- Enhance customer satisfaction
- Effective problem solving
- Process efficiency, etc.
Useful Post:
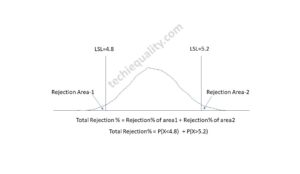
Normal Distribution Probability Formula, Calculation & Manufacturing Examples
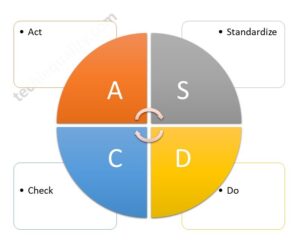
SDCA Cycle understanding with Manufacturing Example | PDCA vs SDCA
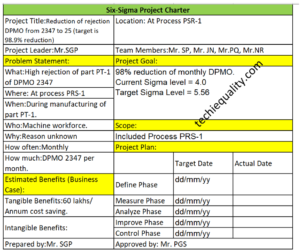
Six Sigma Project Charter Template
CAPA Example | Manufacturing examples | CAPA Meaning
More on TECHIEQUALITY