Quality Assurance Template | 28+ Free QA Template for Practices
Last updated on January 1st, 2024 at 04:18 pm
Quality Assurance Template | 28+ Free QA Template for Practices
Hello readers! Today we are going to discuss on an important topic which is related to the Quality Assurance Process. There are small and big problems in every company or organization and if you would like to solve them or want to improve your process then as a Quality Assurance Engineer you can take improvement projects to meet your target value. But you have to apply methodology, principles, and different tools for systematic continuous improvement, hence here we will learn many methodology and statics tools of QA. Details of 28+ Quality Assurance Template are given below for your practices and knowledge enhancement purposes.
What is Quality Assurance?
QA or Quality Assurance is a systematic approach to ensure that a product/ item or service meets specified requirements which are mentioned in SOP, Standard, Customer specific requirements, Drawing, WP, etc. QA is Proactive and its team operates proactively so the main purpose is to prevent defects/ quality issues/waste/ scrap/ rework and to ensure that the final product/output meets the quality requirement/ standard/ CSR. It enhances customer satisfaction by assuring the CSR and their need & expectations.
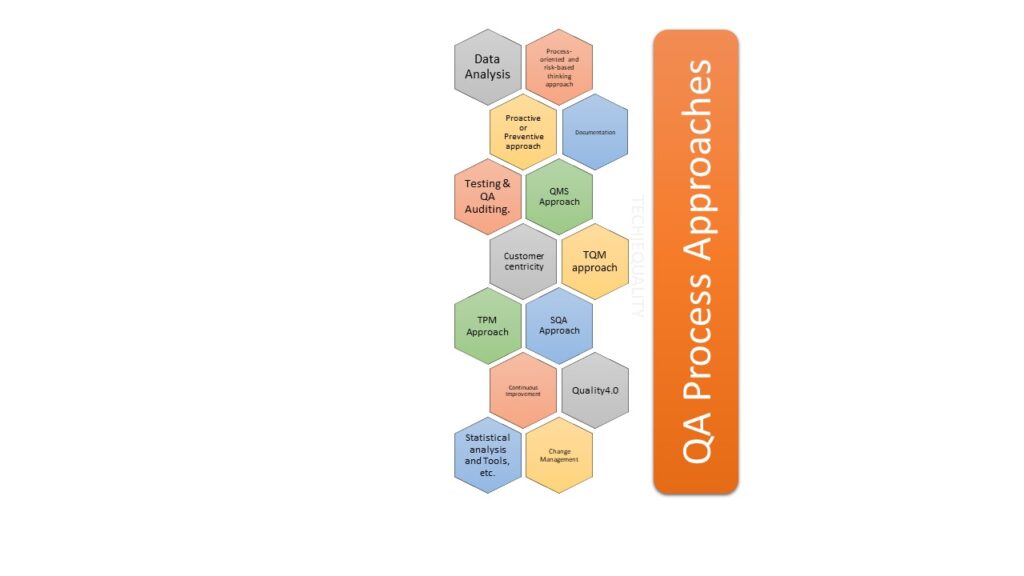
Below are some major key approaches to QA process or activities
- Process-oriented and risk-based thinking approach
- Proactive or Preventive approach
- QMS Approach
- Customer centricity
- SQA Approach
- Continuous Improvement
- Change Management
- Documentation
- Testing & QA Auditing.
- Data Analysis
- TQM approach
- TPM Approach
- Quality4.0
- Statistical analysis and Tools, etc.
Process-oriented and risk-based thinking approach:
Starting from product development to dispatch, you should establish the standard and procedure to ensure the quality standard in every stage. Involvement of QA is necessary for the process approach and similarly, we have to identify the risk associated with it to prevent Quality damage.
Proactive or Preventive approach:
In This approach, you have to be more active in preventing defects, quality issues, rework reduction, waste reduction, etc. rather than identifying them after they occur. Quality assurance plan or control plan preparation and full-phase implementation to prevent any type of quality issue is first priority. You have to give more attention to adherence to standard requirements.
QMS Approach:
The quality management system is the systematic approach for standardizing each activity related to the standard requirements of Iso 9001 and IATF 16949. Implement the all clauses of the standard, document the activities, retain the record, and carry out different types of Audits like QMS audits, Supplier audits, process audits, product audits, layer audits, etc. Doing gap analysis and conducting the management review for an action plan and allocating the resource requirement is the next level of QA activities. So it’s a systematic and effective approach to QA.
Customer centricity:
Customer is king for every organization and business, so converting the customer requirement to objective and Process or product characteristics to meet their requirement is one of the major activities of the QA process. SRM (Supplier relationship management), customer-specific requirements, warranty analysis, customer enhancement, customer feedback, customer satisfaction in scorecard monitoring, and customer complaint management are those activities that you have to give more emphasis on it.
SQA Approach:
Like in-house processes, your outsourcing and Supplier activities are also important to ensure as per your business requirements. Incoming material, BOP, and service of supplier can directly or indirectly affect your product quality or hamper the in-process quality as well. The major activities involved in SQA are supplier development, enlistment, supplier rating, supplier auditing, incoming material testing, BOP part testing and inspection, etc.
Continuous Improvement:
The process is a dynamic activity, and there is always a scope for improvement. Continuous improvement is not a one-time activity but it’s an ongoing process towards quality improvement. You can gather the issues, quality problems, and suggestions through a feedback mechanism. There are many tools and techniques that you can follow like 7QC tools, Six Sigma tools, statistical tools, hypothesis tests, KAIZEN, QC, SGA, DMAIC methodology, DOE, Automation, Poka-yoke, PDCA, SDCA, etc. You can involved in reviewing processes and adjusting to improve efficiency and effectiveness.
Change Management:
Design change to process change, or anything is amended then you have to update/revise it on pertinent document and same to be communicated to relevant users like inspector or operators or end workforce for effective result. 4M change management is a very popular change management approach that many organizations following it.
Documentation:
Documentation including maintained and retained Documented information. Each and every process and activity involved are supposed to be in written form in a standardized manner so that you can easily refer to those when you need them for your reference. You can establish a systematic document control mechanism in your organization.
Testing & QA Auditing:
For the process & product verification and validation, the contribution of both testing & auditing is taking the major activities among the whole QA process. testing may vary industries to industry, process to process, and product to product range but it is a very useful process for monitoring the performance and confirming the product quality. There are so many auditing types like process audit, product audit, layer audit, QMS audit, Autopsy audit, etc. According to the requirement you can select the audit types.
Data Analysis:
The heart of the QA process is Data Analysis and its interpretation. Your decision-making on quality is directly related to data analysis and its correct and accurate interpretation of results. The complete data analysis process is given below; (step-by-step guide to do the data analysis).
- Data collection from sources like shop floor operation, different operations, testing, auditing, feedback, etc.
- Selection of data type
- Normality test
- Selection of tools, techniques, tests, graphs, charts, etc.
- Interpret the test result, graph, or chart.
- Identify the significant cause, if applicable
- Do the Why-Why analysis.
- Identify the Root Cause
- Prepare the Proposed action plan
- Do the trial implementation
- Compare the result with the standard
- Do the final implementation.
- Compare the result
- Standardize the process
Above is the complete step-by-step guide to doing the data analysis related to quality defects, damage, problems, issues, complaints, risks, and also for continuous improvement.
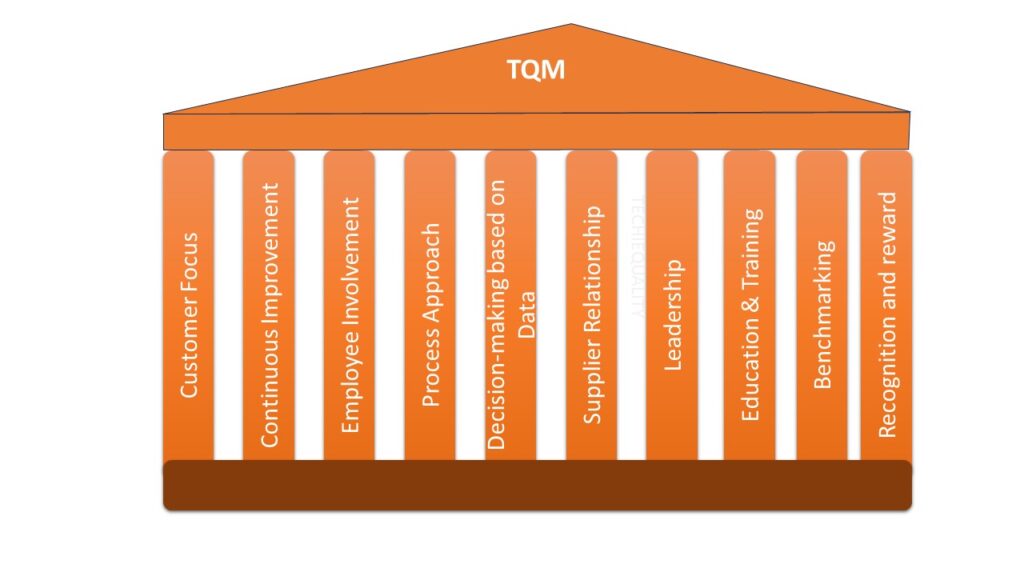
TQM Approach:
Total Quality Management is a management approach that is focused on continuous improvement. TQM is involved in all steps and activities of the organization to enhance quality at every stage of the business.
The main three management for TQM activities are [1] Policy management, [2] Daily management, and [3] Cross function management. The key components of TQM are given below;
- Customer Focus
- Continuous Improvement
- Employee Involvement
- Process Approach
- Decision-making based on Data
- Supplier Relationship
- Leadership
- Education & Training
- Benchmarking
- Recognition and reward.
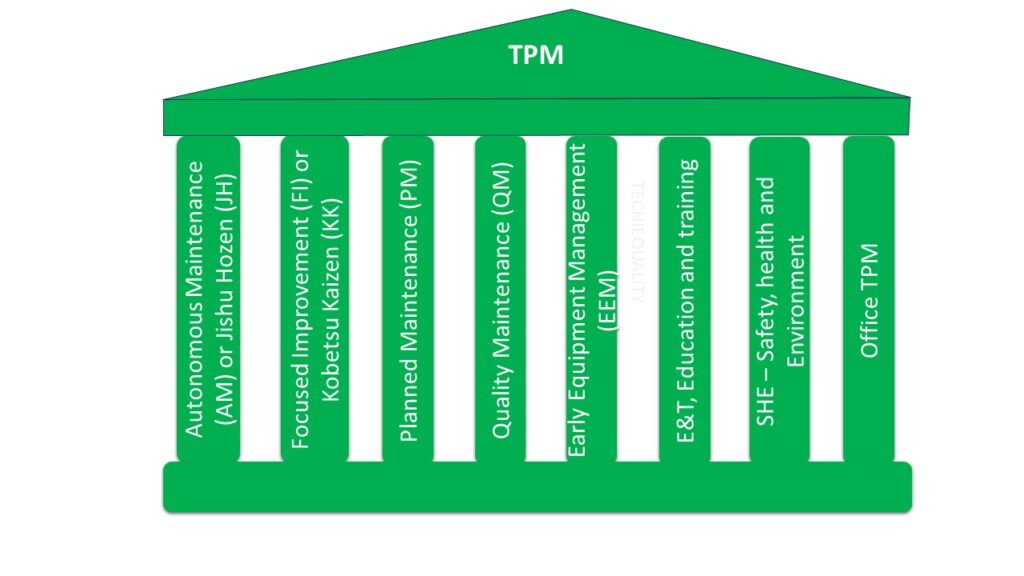
TPM Approach:
The main objective of Total Productive maintenance is to achieve Zero BAD (Zero breakdowns, Zero Accidents, Zero Defects). The main focus of TPM is to maximize the effectiveness and efficiency of machines or equipment. It also emphasizes the proactive and cooperative involvement of all employees.
- OEE – Overall equipment effectiveness.
- Planned Maintenance
- Autonomous Maintenance
- Focused Improvement
- E&T – Education, Training & skill development
- Quality Maintenance
- Early Equipment Management.
- SHE – Safety, Health and Environment.
TPM has one Base pillar, which is called 5’S, and 08 main pillars.
08 Pillars of TPM:
- Autonomous Maintenance (AM) or Jishu Hozen (JH)
- Focused Improvement (FI) or Kobetsu Kaizen (KK)
- Planned Maintenance (PM)
- Quality Maintenance (QM)
- Early Equipment Management (EEM)
- E&T – Education and training
- SHE – Safety, health and Environment
- Office TPM.
Quality4.0:
In this digital era, every organization trying to implement an automation system with fully digitally controls the operation. As we are aware like Industry4.0, Quality4.0 also contributes towards smart factory operation. The main purpose of Quality4.0 is real-time monitoring, digitalization, QA and QC through Smart technology, Robotics involvement, Data Analysis through AI and ML, and Remote controlling of QA/QC by IOT application.
Key Features of Quality4.0 are;
- Data Integration
- Advanced Analytics
- Smart Maintenance
- Real-Time Monitoring
- Traceability & Transparency
- QC/QA Automation
Statistical Analysis and Tools:
The statistical analysis is generally performed through data collection, testing, doing charts/graphs, and interpretation of results. In the manufacturing industry, we commonly use the SPC and Statistical Tests to perform the statistical Analysis.
SPC- Statistical Process control:
SPC are mainly classified into two types and these are;
- Control Chart
- Process Capability.
The Control Chart is further classified into again two types [1] Attribute type Control Chart, [2] Variable Type Control Chart.
Attribute Type Control Chart are:
- NP chart
- P chart
- U chart
- C chart
Variable Type Control Chart are:
- I-MR chart
- X bar R chart
- X bar S chart
Quality Assurance (QA) vs Quality Control (QC):
| QA | QC |
| Aim to prevent defects | Involve in checking and verifying |
| It is Proactive | It’s a reactive |
| Focuses on Process improvement, standard adherence | Focuses on product inspection, and verification |
| Example: Process review, Auditing, Training, documentation, standardization, RCA, etc. | Example: Inspection, verification, testing, |
Benefits of Quality Assurance:
Implementing QA in an organization can give you several benefits and some of the major points are mentioned below;
- Improved Product Quality.
- Enhance customer satisfaction
- Improved the Process
- Cost saving
- Increased the productivity
- Reduced the waste/scrap
- Risk Management
- Brand reputation
- Competitive advantage
- Better decision making
- Continuous Improvement.
28+ Quality Assurance Template for Practices:

As we learned from this article to better manage the QA activities in an organization we are supposed to know the advanced level of concept of several QA Tools, Techniques, and Methodology in terms of application, analysis, and its result interpretation. Following below are some popular and useful Quality Assurance Template are given for your advanced level of learning and practice.
- Six-Sigma Project Charter template
- DMAIC Tools
- SIPOC Template
- C-Chart Excel Template
- DPMO & DPPM excel Calculator
- PFD Excel Format
- Z-Score Excel Calculator Template
- KAIZEN Report Template
- MTTR & MTBF Template
- Scatter Diagram Template
- Dispersion Analysis C&E Template
- 3MU (MUDA) Check Sheet
- 4M Checklist
- FTA Template
- Pp & Ppk Template
- Cp & Cpk Template
- CAPA Format.
- Pareto Chart Template.
- Fishbone Diagram Template.
- Histogram Template
- 8D template.
- Control Chart Template.
- Run Chart Excel Template.
- Risk Identification Template.
- OEE Calculation Format
- SWOT Analysis Template
- 5W1H Template
- 5W2H Template
- P Chart Template
- 5 Whys Excel Template
I hope all 30 Quality Assurance Templates are useful to you and you have completely learned the concept and application.